Construction Laborer
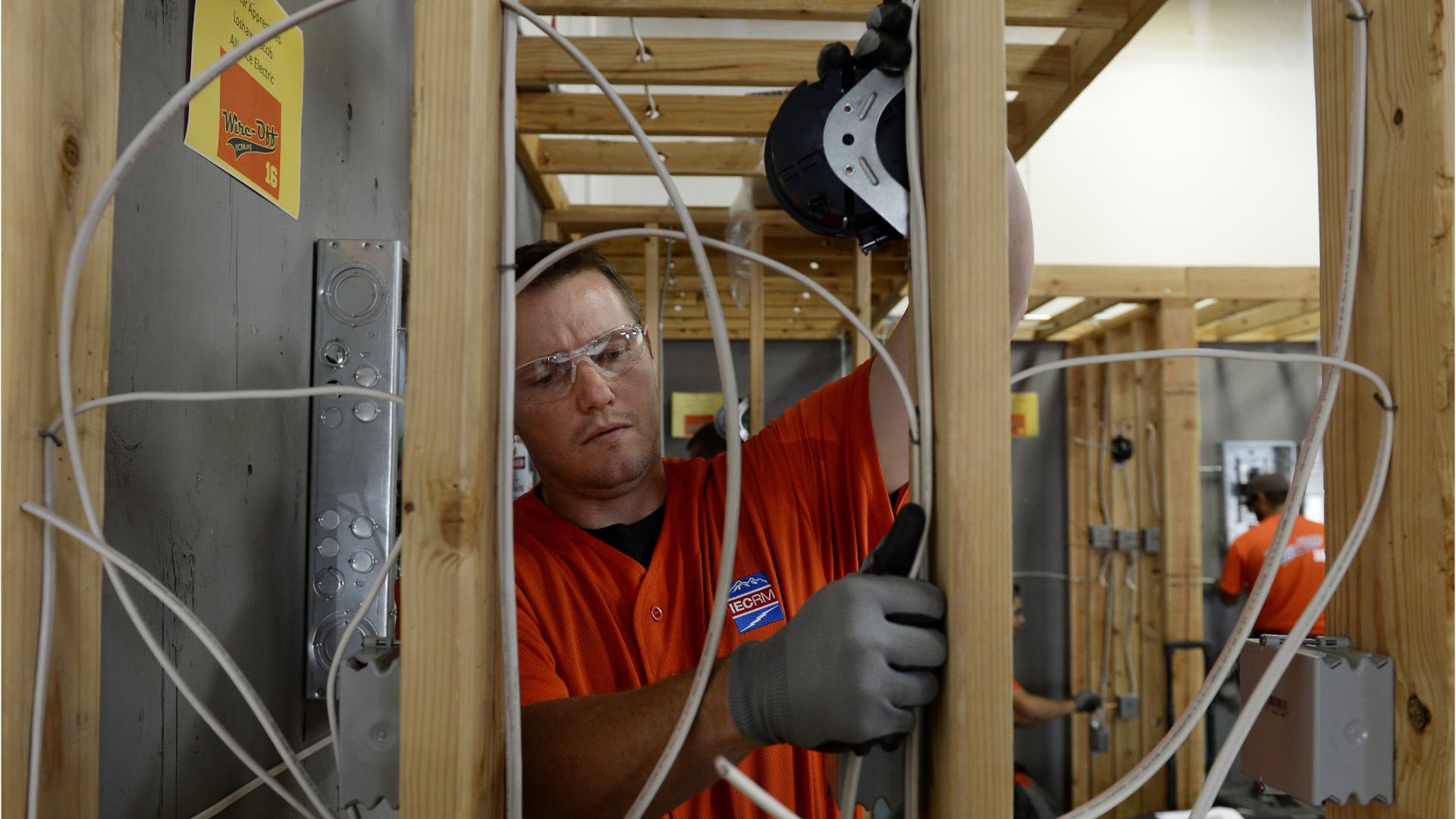
Construction Laborer
Career Overview
A construction laborer performs various tasks on construction sites including removing debris, moving around construction materials, digging trenches or holes, constructing scaffolding, along with many other construction-related tasks.
Education
There is no formal educational requirement for becoming a construction laborer. This job is generally learned through on-the-job training, possibly in conjunction with a formal apprenticeship program.
Future Outlook
Overall employment of construction laborers and helpers is projected to grow 5 percent from 2019 to 2029, faster than the average for all occupations. Construction laborers work in all fields of construction, and demand for laborers should mirror the level of overall construction activity.
Work Environment
Construction laborers work within every aspect of the construction industry and are often required to do physically demanding work. Some work at great heights or outdoors in all weather conditions. In terms of the rate of injuries, this may be one of the most dangerous of all occupations.
Recommended High School Courses
- Communication
- Trade-related courses
- Physical Education
- Active Listening - Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
- Coordination - Adjusting actions in relation to others' actions.
- Operation and Control - Controlling operations of equipment or systems.
- Operation Monitoring - Watching gauges, dials, or other indicators to make sure a machine is working properly.
- Speaking - Talking to others to convey information effectively.
- Building and Construction - Knowledge of materials, methods, and the tools involved in the construction or repair of houses, buildings, or other structures such as highways and roads.
- Mechanical - Knowledge of machines and tools, including their designs, uses, repair, and maintenance.
- Public Safety and Security - Knowledge of relevant equipment, policies, procedures, and strategies to promote effective local, state, or national security operations for the protection of people, data, property, and institutions.
- Arm-Hand Steadiness - The ability to keep your hand and arm steady while moving your arm or while holding your arm and hand in one position.
- Category Flexibility - The ability to generate or use different sets of rules for combining or grouping things in different ways.
- Control Precision - The ability to quickly and repeatedly adjust the controls of a machine or a vehicle to exact positions.
- Deductive Reasoning - The ability to apply general rules to specific problems to produce answers that make sense.
- Depth Perception - The ability to judge which of several objects is closer or farther away from you, or to judge the distance between you and an object.
- Dynamic Strength - The ability to exert muscle force repeatedly or continuously over time. This involves muscular endurance and resistance to muscle fatigue.
- Extent Flexibility - The ability to bend, stretch, twist, or reach with your body, arms, and/or legs.
- Far Vision - The ability to see details at a distance.
- Finger Dexterity - The ability to make precisely coordinated movements of the fingers of one or both hands to grasp, manipulate, or assemble very small objects.
- Information Ordering - The ability to arrange things or actions in a certain order or pattern according to a specific rule or set of rules (e.g., patterns of numbers, letters, words, pictures, mathematical operations).
- Manual Dexterity - The ability to quickly move your hand, your hand together with your arm, or your two hands to grasp, manipulate, or assemble objects.
- Multilimb Coordination - The ability to coordinate two or more limbs (for example, two arms, two legs, or one leg and one arm) while sitting, standing, or lying down. It does not involve performing the activities while the whole body is in motion.
- Near Vision - The ability to see details at close range (within a few feet of the observer).
- Oral Comprehension - The ability to listen to and understand information and ideas presented through spoken words and sentences.
- Oral Expression - The ability to communicate information and ideas in speaking so others will understand.
- Problem Sensitivity - The ability to tell when something is wrong or is likely to go wrong. It does not involve solving the problem, only recognizing there is a problem.
- Rate Control - The ability to time your movements or the movement of a piece of equipment in anticipation of changes in the speed and/or direction of a moving object or scene.
- Selective Attention - The ability to concentrate on a task over a period of time without being distracted.
- Speech Clarity - The ability to speak clearly so others can understand you.
- Speech Recognition - The ability to identify and understand the speech of another person.
- Stamina - The ability to exert yourself physically over long periods of time without getting winded or out of breath.
- Static Strength - The ability to exert maximum muscle force to lift, push, pull, or carry objects.
- Trunk Strength - The ability to use your abdominal and lower back muscles to support part of the body repeatedly or continuously over time without 'giving out' or fatiguing.
- Operate pumps or compressors.
- Clean equipment or facilities.
- Maintain construction tools or equipment.
- Signal equipment operators to indicate proper equipment positioning.
- Install plumbing or piping.
- Position structural components.
- Install green structural components, equipment or systems.
- Direct vehicle traffic.
- Review blueprints or specifications to determine work requirements.
- Finish concrete surfaces.
- Test air quality at work sites.
- Clean work sites.
- Compact materials to create level bases.
- Dig holes or trenches.
- Mark reference points on construction materials.
- Measure work site dimensions.
- Assemble temporary equipment or structures.
- Dismantle equipment or temporary structures.
- Load or unload materials used in construction or extraction.
- Move construction or extraction materials to locations where they are needed.
- Install insulation in equipment or structures.
- Assist skilled construction or extraction personnel.
- Apply paint to surfaces.
- Apply sealants or other protective coatings.
- Clean surfaces in preparation for work activities.
- Remove worn, damaged or outdated materials from work areas.
- Position construction forms or molds.
- Smooth surfaces with abrasive materials or tools.
- Install masonry materials.
- Protect structures or surfaces near work areas to avoid damage.
- Mix substances or compounds needed for work activities.
- Break up rock, asphalt, or concrete.
- Pour materials into or on designated areas.
- Spread concrete or other aggregate mixtures.
- Prepare hazardous waste for processing or disposal.
- Operate heavy-duty construction or installation equipment.
Potential Scholarships
Approx Salary Expectation
References
Trend Analysis - Explorer the Market, Labour Market Information, Government of Canada https://www.jobbank.gc.ca/trend-analysis.
O*NET OnLine, National Center for O*NET Development, https://www.onetonline.org/.